Table of Contents
Java LinkedHashSet
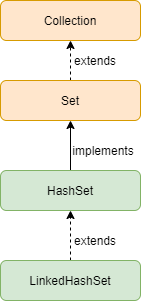
Java LinkedHashSet implements the Set interface and extends the HashSet class. It uses the implementation of a doubly-linked list on the hashtable. This means it maintains the insertion order while iterating through the elements. We can retrieve the elements in the same order we insert it.
Features of Java LinkedHashSet
Below are the important features of the Java LinkedHashSet:
- We can store only unique elements in a LinkedHashSet.
- Ability to retrieve the elements in the same order we insert
- Non-synchronized.
- Allows storing null elements.
- Uses hashing technique to store elements at the specified index based on the hashcode.
Hierarchy
Constructors
Below are the constructors which we can use for the Java LinkedHashSet class.
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| LinkedHashSet() | Creates a default LinkedHashSet |
| LinkedHashSet(int capacity) | Creates a LinkedHashSet with specified capacity |
| LinkedHashSet(int capacity, float loadFactor) | Creates a LinkedHashSet with the specified capacity and load factor. |
| LinkedHashSet(Collection c) | Creates a LinkedHashSet with the specified collection |
Methods
The below methods are supported by the Java LinkedHashSet class.
| Method | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| boolean add(Object e) | Adds the specified element to the set | e - The element to be added Returns true if the element is not present already Returns false if element is already present |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | Adds all the elements in the specified collection | c - collection that contains elements to add |
| void clear() | Removes all the elements in the set and makes the set empty | |
| Object clone() | Returns a shallow copy of the TreeSet instance | |
| boolean contains(Object o) | Returns true if the set contains the specified element | o - the element to search |
| boolean containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if the set contains all elements specified in the collection | c - collection elements to search |
| boolean equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object in the set | Returns true if present Returns false if not present |
| boolean isEmpty() | Returns true if the set is empty and does not contain any elements | |
| Iterator iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in the ascending order | |
| boolean remove(Object o) | Removes the specified element from the set | o - the element to be removed |
| boolean removeAll(Collection c) | Removes all the elements in the specified collection | c - the collection of elements to be removed |
| boolean retainAll(Collection c) | Retains all the elements in the specified collection in the set and removes the other elements in the Set | c - the collection of elements to be retained |
| int size() | Returns the size of the set that is the number of elements in the set | |
| Spliterator spliterator() | Returns the spliterator over the elements in the set | |
| Object[] toArray() | Returns an array representation of the elements in the set | |
| String toString() | Returns a string representation of the elements in the set |
Example: Add elements to the LinkedHashSet
We can add elements to the Set using the add() method and add a collection using the addAll() method.
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class AddElementsLinkedHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<Integer> lh = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
lh.add(20);
lh.add(30);
lh.add(10);
lh.add(50);
lh.add(40);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after add method: " + lh);
LinkedHashSet<Integer> l = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
l.add(60);
l.add(80);
lh.addAll(l);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after addAll method: " + lh);
}
}
Elements in the Set after add method: [20, 30, 10, 50, 40] Elements in the Set after addAll method: [20, 30, 10, 50, 40, 60, 80]
Example: Delete elements from the LinkedHashSet
Below is the example that shows how to delete elements from the Set. To remove a specific value we can use the remove() method and remove all the values, use the removeAll() method. We can retain only the collection and remove the others from the Java LinkedHashSet using the retainAll() method.
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class RemoveElementsLinkedHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<Integer> lh = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
lh.add(20);
lh.add(30);
lh.add(10);
lh.add(50);
lh.add(40);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after add method: " + lh);
lh.remove(50);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after remove method: " + lh);
lh.removeAll(lh);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after removeAll method: " + lh);
lh.add(10);
lh.add(20);
LinkedHashSet<Integer> l = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
l.add(60);
l.add(80);
lh.addAll(l);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after addAll method: " + lh);
lh.retainAll(l);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after retainAll method: " + lh);
}
}
Elements in the Set after add method: [20, 30, 10, 50, 40] Elements in the Set after remove method: [20, 30, 10, 40] Elements in the Set after removeAll method: [] Elements in the Set after addAll method: [10, 20, 60, 80] Elements in the Set after retainAll method: [60, 80]
Example: Iterate through elements in the LinkedHashSet
There are 2 ways we can iterate through values in the LinkedHashSet in Java. We can use either the iterator() method or use the
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class IterateLinkedHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<String> l = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
l.add("Aditya");
l.add("Banu");
l.add("Sreenath");
l.add("Vivek");
l.add("Rupesh");
System.out.println("Size of the LinkedHashSet: " + l.size());
//Iterate using the iterator
System.out.println("Iterate using the iterator");
Iterator<String> i = l.iterator();
while(i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
System.out.println("Iterate using the for-each");
//Iterate using the for-each loop
for(String s: l)
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Size of the LinkedHashSet: 5 Iterate using the iterator Aditya Banu Sreenath Vivek Rupesh Iterate using the for-each Aditya Banu Sreenath Vivek Rupesh
Example: Clear content in the Set and check if empty
We can clear the contents in the Set by using the clear() method and check if the LinkedHashSet is empty using the isEmpty() method.
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class ClearLinkedHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<String> l = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
l.add("Aditya");
l.add("Banu");
l.add("Sreenath");
l.add("Vivek");
l.add("Rupesh");
System.out.println("Elements in the Set: " + l);
l.clear();
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after using clear method: " + l);
System.out.println("Is LinkedHashSet empty: " + l.isEmpty());
}
}
Elements in the Set: [Aditya, Banu, Sreenath, Vivek, Rupesh] Elements in the Set after using clear method: [] Is LinkedHashSet empty: true
Example: Check for a specific element or a collection of elements
The below example shows how to check if the LinkedHashSet contains a specific value using the contains() method and a collection using the containsAll() method.
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class CheckElementLinkedHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<String> l = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
l.add("Aditya");
l.add("Banu");
l.add("Sreenath");
l.add("Vivek");
l.add("Rupesh");
System.out.println("Elements in the Set: " + l);
System.out.println(l.contains("Sreenath"));
System.out.println(l.contains("Divya"));
LinkedHashSet<String> lh = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
lh.add("Ramya");
lh.add("Sriya");
l.addAll(lh);
System.out.println("Elements in the Set after addAll method: " + l);
System.out.println(l.containsAll(lh));
}
}
Elements in the Set: [Aditya, Banu, Sreenath, Vivek, Rupesh] true false Elements in the Set after addAll method: [Aditya, Banu, Sreenath, Vivek, Rupesh, Ramya, Sriya] true
Example: Convert LinkedHashSet to an array
In the below example, we convert the LinkedHashSet to an array using the toArray() method and print the element at array index 1.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class ConvertToArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<String> l = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
l.add("Aditya");
l.add("Banu");
l.add("Sreenath");
l.add("Vivek");
l.add("Rupesh");
System.out.println("Elements in the Set: " + l);
String[] s = new String[l.size()];
l.toArray(s);
System.out.println("Convert to array:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s));
System.out.println("Display the element at array index 1: " + s[1]);
}
}
Elements in the Set: [Aditya, Banu, Sreenath, Vivek, Rupesh] Convert to array: [Aditya, Banu, Sreenath, Vivek, Rupesh] Display the element at array index 1: Banu
Example: Convert LinkedHashSet to other Set Collections
We can convert LinkedHashSet to other Set Collections like TreeSet, HashSet using the constructor that accepts a collection as a parameter. The below example illustrates how to convert a LinkedHashSet into a TreeSet and a HashSet.
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class ConvertToTreeSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> s = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
s.add("Chennai");
s.add("Bangalore");
s.add("Delhi");
s.add("Mumbai");
System.out.println("LinkedHashSet: " + s);
Set<String> t = new TreeSet<String>(s);
System.out.println("TreeSet: " + t);
Set<String> h = new HashSet<String>(s);
System.out.println("HashSet: " + h);
}
}
LinkedHashSet: [Chennai, Bangalore, Delhi, Mumbai] TreeSet: [Bangalore, Chennai, Delhi, Mumbai] HashSet: [Delhi, Chennai, Mumbai, Bangalore]
Time Complexity
The time complexity of the most commonly used methods like add(), remove(), and contains() is a constant value which is O(1).